Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination involves injecting good quality motile sperms into the female genital tract for the purpose of achieving a pregnancy. Insemination can be done by two methods:
Depending on the provider of the semen sample, artificial insemination could be:-
1. Artificial insemination by husband (AIH) - Where the woman's husband provides the sample by masturbation which is then injected into the woman's uterus
2. Artificial insemination by donor (AID) - Where an anonymous donor's sperm is used usually as a frozen, thawed sample for insemination
Depending on the site of placement of sperms, insemination could be:-
1. Intracervical insemination (ICI) – This involves the deposition of raw fresh or frozen thawed semen into the cervix usually by injecting it with a needleless syringe
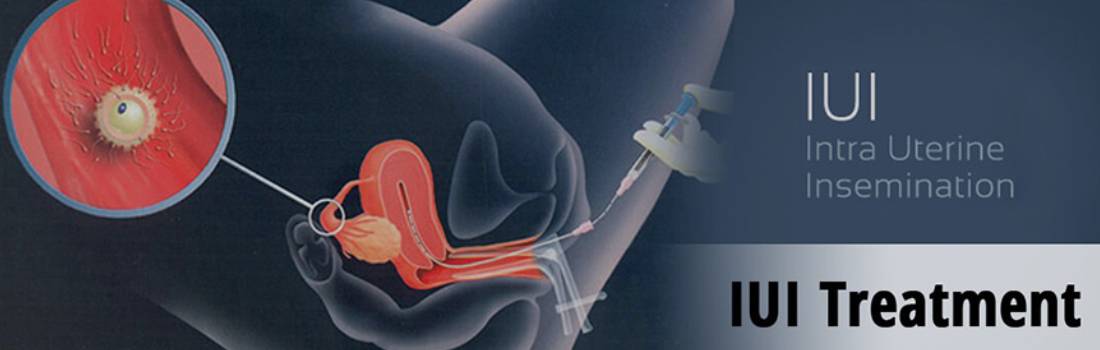
2. Intrauterine insemination (IUI) – Washed sperm, spermatozoa that have been removed from most other components of the seminal fluids, can be injected directly into a women's uterus in a process called intrauterine insemination (IUI). If the semen is not washed, it may elicit uterine cramping, expelling the semen and causing pain, due to content of prostaglandins
A) Indications for Artificial Insemination
AIH
a) MEN
-
Men who are unable to ejaculate in the vagina. The failure of ejaculation can be caused due to diabetes, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury
-
Retograde ejaculation in males where sperms are released backward into the bladder instead of urethra.
- This can be the result of diabetes, trauma or operation in neck of the bladder or a side effect of some medication
-
Men with poor quality sperms or very low sperm count or antisperm antibodies.
-
Men who wish to freeze their sperm for possible future use before vasectomy, chemotherapy or radiotherapy for cancer.
b) Women
-
Women with mild endometriosis
-
Women with cervical mucus hostility or poor cervical mucus
c) Couple
-
Couples with unexplained infertility
B) Artificial Insemination Donor (AID) -
1. Males with azoospermia who cannot afford advanced treatments like ICSI.
2. Males with genetic disorders, where it can be transmitted to the child.
3. It may be used as a backup to the procedure of TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction) and ICSI that is done for males with non-obstructive Azoospermia, especially when no sperms are found in the testicular biopsy.
4. In couples were other ART methods have failed repeatedly.
Prerequisites for undergoing an IUI?
Preferably the patient should:
1. Be less than 38 years of age.
2. Have at least one open fallopian tube. This can be diagnosed by either a Laparoscopy or a Hysterosalpingography.
3. Have a minimum sperm count of at least 10 million or a count following washing of semen of atleast 3-5 million motile sperms per ml.
At Dr. Rama Sofat Hospital & Dr. Ruchika Test tube Baby Centre, we treat patients with less sperm count. In such cases we advocate 3-6 IUI cycles with simultaneous treatment for increasing counts by a male specialist. The success of IUI in patients with very low sperm counts is low. Consequently, those who fail to become pregnant are advised to opt for ICSI or Donor Insemination
Protocols for IUI
The IUI can be done in a natural cycle or stimulated cycle
1. In Natural cycle or unstimulated cycle, IUI is timed to take place at the time of natural ovulation. Ovulation is detected using ovulation predictor kits or serial blood tests or serial ultrasound scans usually between 12 to 16th day of the menstrual cycle
2. In Stimulated Cycle, single or multiple egg formation is achieved through drugs such as Clomiphene Citrate, Gonadotrophins(FSH or HMG) alone or in combination with clomiphene or GnRh analogues. The basic requirement for most ART treatments is formation of more than one mature egg, as this is generally associated with improved chances of conception. The growth of the eggs is observed via vaginal sonography that shows follicle size and count. Occasionally a blood level of serum Estadiol hormone (E2 Level) may be done. Once two leading follicles have reached a size of 1.8- 2 cm, HCG injection is given to bring about ovulation and IUI is done after 36 and 48 hours of giving the injection
IUI at Dr. Rama Sofat Hospital: Normally our unit does 2 IUI cycles using Clomiphene. If this fails to achieve pregnancy, we use a combination of Clomiphene with Gonadotrophins(FSH) and try out 2-3 cycles. If this fails to achieve pregnancy, we try out 2 cycles with pure Gonadotrophin drugs, with or without GnRH analogue. In case this also fails, we go for either IVF or ICSI treatment.
Semen Production:
The husband is given a sterile container, and he is asked to give his semen sample by masturbation in a semen collection room. He can even give the sample at home and reach the clinic within a period of 30 minutes. In case of difficulty in ejaculating, many other options may be tried out but it is necessary not to use any lubricant, including soap for semen production
Semen Preparation:
The semen is processed in the laboratory using specially imported culture media. The semen can be processed and washed either by the standard swim-up method or the density gradient method. The seminal fluid is discarded and the best quality motile sperms are separated. These are then floated in 1/2 to 1 ml of culture media, which is then used for insemination.
Insemination:
The procedure of IUI takes about 2 hours from the time semen is produced till the IUI is done. The patient is placed on the table. Speculum is inserted and cervix exposed. The cervix is cleaned with saline. The sperm suspension is then taken in a syringe to which a thin cannula is attached. The cannula passes through the cervix into the uterine cavity and gently deposits the sperm suspension. The procedure is painless and takes about 5 minutes after which the patient is made to lie for another 15 minutes and then sent home. The rationale for doing an IUI is that the effect of vaginal acidity and cervical mucus hostility can be decreased. A washed sample has more number of highly motile good quality sperms and also the chances of having uterine cramps and infections are significantly reduced.
Success Rate:
The best results are seen among patients with cervical factors and in IUI's done using donor semen. The success rates vary from 15-25% per cycle. This means that after about 6 months of treatment, 4 to 6 patients out of 10 would have become pregnant. The remaining would need advanced procedures like IVF or ICSI to achieve a pregnancy.
POST IUI MEDICINE
Generally following an IUI procedure the patient is given a mild antibiotic along with Luteal support in the form of oral progesterone/varginal pessaries for 2 weeks. After 14 days a blood test (B-HCG) is done to confirm her pregnancy. In case pregnancy ensues luteal support is continued for another 2 weeks.